Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Hydroxy Acids.
 |
deutsche Version. |
| © |
Copyright note. |
 |
Site-map. |
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Hydroxy Acids. |
|
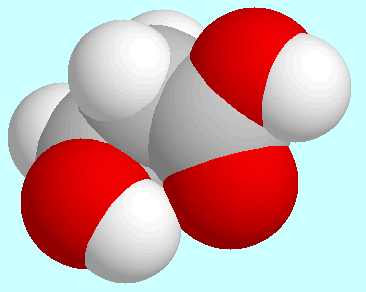
 -hydroxypropionic acid
basically forms the same intramolecular interactions as glycolic acid:
O-H···O=C,
O-H···(CO)O-H, and (CO)O-H···O-H.
The first of these interactions occurs in the global minimum, the
geometry of which is shown next to this paragraph. In this conformer,
the COOH group is coplanar with the plane of the three carbon atoms, and
the aliphatic OH group sticks out of that plane and points towards the
carbonyl oxygen atom. In the resulting interaction, the
H···O-distance
is slightly larger (2.30 Å) than in the corresponding
conformer of glycolic acid. According to an analysis of the electron
density, this interaction is not a hydrogen bond but electrostatic in nature.
-hydroxypropionic acid
basically forms the same intramolecular interactions as glycolic acid:
O-H···O=C,
O-H···(CO)O-H, and (CO)O-H···O-H.
The first of these interactions occurs in the global minimum, the
geometry of which is shown next to this paragraph. In this conformer,
the COOH group is coplanar with the plane of the three carbon atoms, and
the aliphatic OH group sticks out of that plane and points towards the
carbonyl oxygen atom. In the resulting interaction, the
H···O-distance
is slightly larger (2.30 Å) than in the corresponding
conformer of glycolic acid. According to an analysis of the electron
density, this interaction is not a hydrogen bond but electrostatic in nature.
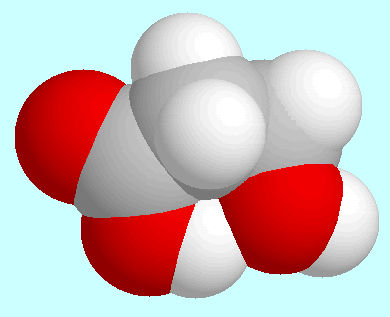
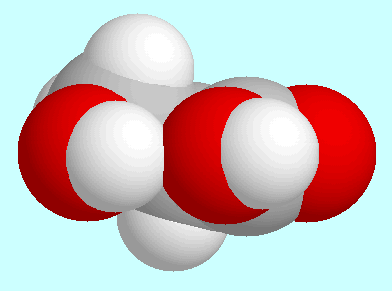 The geometry of the conformer of second lowest energy,
which is shown next to this paragraph, is characterized by a COOH group
that is coplanar with the aliphatic OH group. The carbon atoms
The geometry of the conformer of second lowest energy,
which is shown next to this paragraph, is characterized by a COOH group
that is coplanar with the aliphatic OH group. The carbon atoms
 and
and
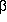 are located above and below this plane, respectively.
The O-H···O-H-interaction in this conformer
is a true hydrogen bond,
which is weak, however: the H···O distance is
2.15 Å and the bond order is 0.023.
Hence, there is no stabilization associated with this H-bond: the
relative energy of this conformer is 7.2 kJ/mol.
are located above and below this plane, respectively.
The O-H···O-H-interaction in this conformer
is a true hydrogen bond,
which is weak, however: the H···O distance is
2.15 Å and the bond order is 0.023.
Hence, there is no stabilization associated with this H-bond: the
relative energy of this conformer is 7.2 kJ/mol.
 The (CO)O-H···O-H-interaction is
a much stronger hydrogen bond with a
bond order of 0.062 and a H···O-distance
of 1.84 Å;
this value is significantly lower than the one in the corresponding
conformer of glycolic acid (1.97 Å), which would indicate a
stronger H-bond. The kinetic stability, however, is lower than in glycolic
acid: the smallest potential barrier is 27 kJ/mol and can be found
in two different reaction paths (with almost identical values). The first
of these reaction paths corresponds to the conversion of this conformer
to its mirror image, the second corresponds to a combined rotation of the
COOH- and the aliphatic OH-group and results in a conformer that is
identical with the global minimum, except for the
trans-orientation of the COOH group.
The potential energy surface of
The (CO)O-H···O-H-interaction is
a much stronger hydrogen bond with a
bond order of 0.062 and a H···O-distance
of 1.84 Å;
this value is significantly lower than the one in the corresponding
conformer of glycolic acid (1.97 Å), which would indicate a
stronger H-bond. The kinetic stability, however, is lower than in glycolic
acid: the smallest potential barrier is 27 kJ/mol and can be found
in two different reaction paths (with almost identical values). The first
of these reaction paths corresponds to the conversion of this conformer
to its mirror image, the second corresponds to a combined rotation of the
COOH- and the aliphatic OH-group and results in a conformer that is
identical with the global minimum, except for the
trans-orientation of the COOH group.
The potential energy surface of 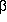 -hydroxypropionic acid contains a total of
16 symmetry-unique conformers.
Seven out of these 16 are lower in energy than
this H-bonded conformer (Erel=16.7 kJ/mol), which is
another indication for the minor stabilization due to the hydrogen bond.
A numerical estimate confirms this by yielding a stabilization energy
of 36.6 kJ/mol for
-hydroxypropionic acid contains a total of
16 symmetry-unique conformers.
Seven out of these 16 are lower in energy than
this H-bonded conformer (Erel=16.7 kJ/mol), which is
another indication for the minor stabilization due to the hydrogen bond.
A numerical estimate confirms this by yielding a stabilization energy
of 36.6 kJ/mol for 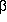 -hydroxypropionic acid, but 54.4 kJ/mol for glycolic acid.
-hydroxypropionic acid, but 54.4 kJ/mol for glycolic acid.
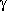 -hydroxybutyric acid.
-hydroxybutyric acid.