Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Amino Aldehydes.
 |
deutsche Version. |
| © |
Copyright note. |
 |
Site-map. |
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Amino Aldehydes. |
|
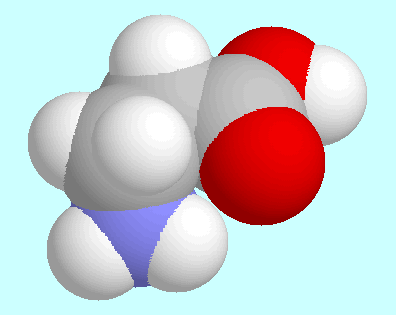
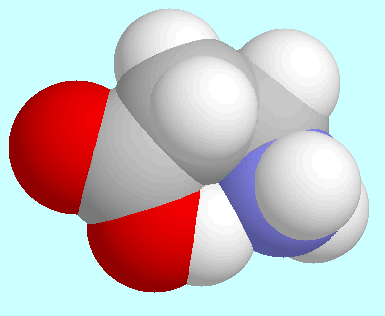
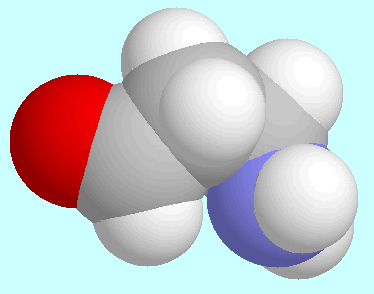
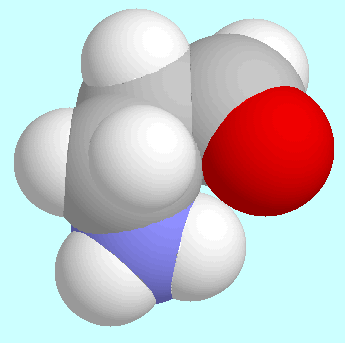 The comparison between
3-aminopropanal and
The comparison between
3-aminopropanal and  -alanine reveals
a surprising amount
of similarity between the geometries of the various conformers.
The two global minima, for instance, which are shown next to this paragraph,
are virtually identical except for the intended difference
that the OH-group of the acid is replaced by a
hydrogen atom in the aldehyde. This similarity also includes
the N-H···O=C interaction, which in both cases is an
attractive electrostatic interaction but no hydrogen bond.
-alanine reveals
a surprising amount
of similarity between the geometries of the various conformers.
The two global minima, for instance, which are shown next to this paragraph,
are virtually identical except for the intended difference
that the OH-group of the acid is replaced by a
hydrogen atom in the aldehyde. This similarity also includes
the N-H···O=C interaction, which in both cases is an
attractive electrostatic interaction but no hydrogen bond.
 Astonishingly, this similarity even extends to the
conformers with the strongest intramolecular interactions,
which are displayed next to this paragraph. They are the conformer
with the electronically repulsive C-H···N interaction
in the 3-aminopropanal case and the conformer with the highly attractive
intramolecular N···H-O
hydrogen bond in the
Astonishingly, this similarity even extends to the
conformers with the strongest intramolecular interactions,
which are displayed next to this paragraph. They are the conformer
with the electronically repulsive C-H···N interaction
in the 3-aminopropanal case and the conformer with the highly attractive
intramolecular N···H-O
hydrogen bond in the 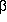 -alanine case.
Despite the totally different nature of these two interactions,
both conformers exhibit an identical orientation of the molecular backbone.
-alanine case.
Despite the totally different nature of these two interactions,
both conformers exhibit an identical orientation of the molecular backbone.
Furthermore, the relative energies of the matching conformers
run parallel too, except for two 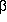 -alanine conformers, which
differ in energy only by 0.017 kJ/mol.
-alanine conformers, which
differ in energy only by 0.017 kJ/mol.