Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Amino Acids.
 |
deutsche Version. |
| © |
Copyright note. |
 |
Site-map. |
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds in Amino Acids. |
|
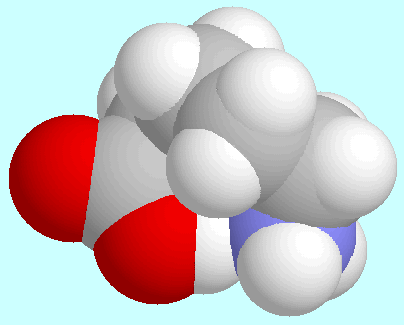
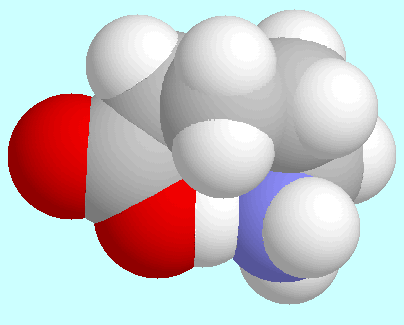
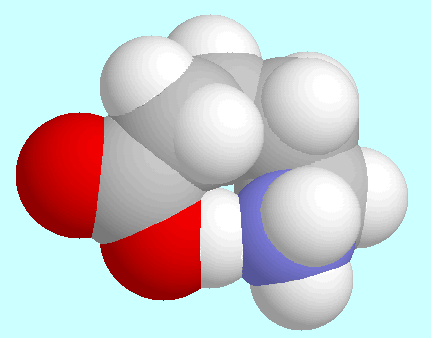
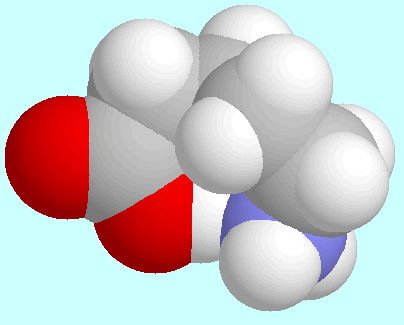
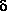 -aminopentanoic acid
forms a total of eight conformers with O-H···N
hydrogen bonds, i.e., four pairs of enantiomers.
The strength of the hydrogen bond
is quite different among these conformations.
Similar to 5-aminopentanol and
-aminopentanoic acid
forms a total of eight conformers with O-H···N
hydrogen bonds, i.e., four pairs of enantiomers.
The strength of the hydrogen bond
is quite different among these conformations.
Similar to 5-aminopentanol and
 -hydroxypentanoic acid, but
in contrast to many other systems, the various criteria
for hydrogen bond strength
that can be obtained from ab initio calculations
(N···H distance;
increase of O-H distance;
decrease of O-H vibration frequency;
deviation of the N···H-O angle from linearity;
electron density of the H-bond;
Hartree-Fock energies, with or without vibrational zero-point
correction) do not give the same ranking in all cases, but lead to
three different rankings. Comparison with the corresponding values
of adducts between propionic acid and ethylamine
H
-hydroxypentanoic acid, but
in contrast to many other systems, the various criteria
for hydrogen bond strength
that can be obtained from ab initio calculations
(N···H distance;
increase of O-H distance;
decrease of O-H vibration frequency;
deviation of the N···H-O angle from linearity;
electron density of the H-bond;
Hartree-Fock energies, with or without vibrational zero-point
correction) do not give the same ranking in all cases, but lead to
three different rankings. Comparison with the corresponding values
of adducts between propionic acid and ethylamine
H C-CH
C-CH -COOH···NH
-COOH···NH -CH
-CH -CH
-CH ,
in which the COOH group is on cis-orientation too,
shows that the eight-membered ring in
,
in which the COOH group is on cis-orientation too,
shows that the eight-membered ring in  -aminopentanoic acid is practically free of ring strain.
-aminopentanoic acid is practically free of ring strain.
 As in
As in 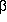 -alanine
and GABA, there
are reaction paths between these conformers that preserve the hydrogen
bond. It turns out that each of the H-bonded conformers may choose
among three different of these reaction paths.
This gives an interesting progression for the number of H-bonded conformers
and the number of H-bond conserving reactions in
the series of the
-alanine
and GABA, there
are reaction paths between these conformers that preserve the hydrogen
bond. It turns out that each of the H-bonded conformers may choose
among three different of these reaction paths.
This gives an interesting progression for the number of H-bonded conformers
and the number of H-bond conserving reactions in
the series of the  -amino acids,
as outlined in the following table.
-amino acids,
as outlined in the following table.
compound conformers non-equivalent reac-
tions per conformer
glycine 1 -
beta-alanine 2 1
gamma-aminobutyric acid 4 2
delta-aminopentanoic acid 8 3
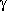 -amino butyric acid.
-amino butyric acid. -aminohexanoic acid.
-aminohexanoic acid.